SMM Network News:
1. Copper strip is the highest barrier area in copper processing industry. As an important downstream of copper plate and strip, connectors consume a large amount of plate and strip. As the chip carrier of the integrated circuit, the lead frame also belongs to the connector. With the help of bonding materials, it realizes the electrical connection between the leading end of the internal circuit of the chip and the external wire, and acts as a bridge to connect with the external wire. Lead frame and manufacturing and packaging application requirements, in addition to high strength, high thermal conductivity, but also requires good brazing, stamping, etching and oxide particle adhesion and so on. It is often made of copper-iron system, copper-nickel-silicon system C70250 and so on.
2.Cu-Ni-Si and Cu-Cr-Zr alloy strips belong to medium-high strength and high electrical conductivity alloys. Domestic Bowei alloy can be mass produced, while Xingye Shengtai Copper can mass produce Cu-Ni-Si alloy. Beryllium copper (Cu-Be) can only be produced by oriental tantalum industry in China, but can not be supplied by Cu-Ti domestic companies. In particular, Cu-Ni-Si alloy has been widely used in the electronic field because of its excellent high temperature stability.
3. Cu-Ni-Si alloy has excellent comprehensive properties, high permeability and great potential. The miniaturization of electronic products and the increasing trend of carrying capacity are obvious. In high current connection situations, such as base station power connectors, new energy vehicle connectors and smart phone connectors, high conductive copper-nickel-silicon alloy can restrain heat and temperature rise, forming a strong substitute for other copper alloys, such as brass, tin-phosphorus bronze and so on.
4. Car connectors are more heat-resistant than smartphones. The temperature environment inside the car: engine 120 ℃, engine surface 135 ℃, dashboard surface 120 ℃, interior floor 105 ℃, rear deck 117 ℃. When people ride in a car without air conditioning, the temperature inside the car can reach 120 ℃. The choice of brass and tin-phosphorus bronze for automobile connectors has been unable to meet the requirements. Titanium-copper or copper-nickel-silicon with better stress relaxation resistance should be used. At present, titanium and copper are only produced abroad, and the processing fee is as high as 200000 yuan / ton. The processing fee of copper, nickel and silicon is 20-30,000 yuan / ton, which has obvious advantage of comprehensive performance-to-price ratio.
5. C42500, C41125, PW33520 (exclusive patent product of Bowei alloy) and other high-performance and low-cost products have been developed at home and abroad to replace tin-phosphorus bronze. Among them, the PW33502 alloy developed in China has a yield strength of 570Mpa and a conductivity of 34%, which is twice that of the original C5191, and can meet the requirements of high transmission and low temperature rise. The bending performance of the bad direction is also better than that of the original C5191. The tin content is lower than that of C5191, and the corner material of tin and nickel plating can be recycled. Compared with tin-phosphorus bronze, the comprehensive performance is excellent and the performance-to-price ratio is high.
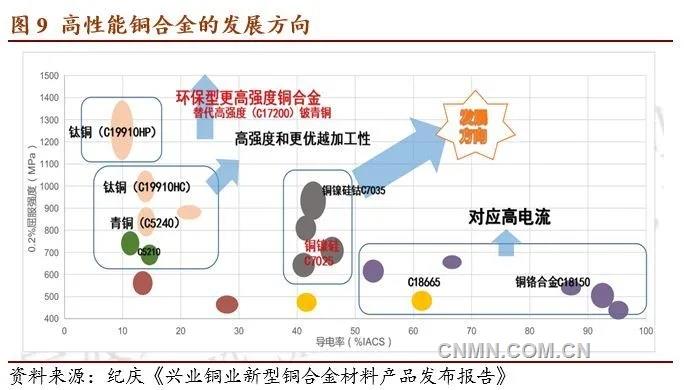
6. China's copper processing industry has gone through three stages, and now it has entered the stage of high-performance materials represented by C7025. To meet the needs of communications, electronics and automotive industries. Xingye Shengtai Copper has developed C7026 and C7035 copper-nickel-silicon materials. C7035 has excellent properties and can partially replace low beryllium copper alloy.
7. C18150amp C18400Murray-strength 600MPa has both the electrical conductivity of 85%IACS and the thermal conductivity of 330W/ (m ·k). It is the most ideal copper alloy in the region of high electrical conductivity and medium strength, and has very high stress relaxation and high temperature softening resistance. Applications: high current connectors, oil-electric hybrid charge and discharge connectors, battery fast charge and flash charge, high power relays, terminals and efficient thermal management solutions.
8. The development of high performance copper alloy in the future may have the following four directions: (1) double 70 alloy, tensile strength 700MPa, electrical conductivity 70%IACS, thickness 0.03-0.06mm; (2) environment-friendly materials, tensile strength > 1000 MPa, yield strength > 950mm, electrical conductivity > 45% IACS; (3) new composite materials, making use of the characteristics and advantages of various metals, to improve the comprehensive properties and optimize the cost. (4) Magnetic conductive materials, CFA copper-iron alloy products, the general iron content is 15-50%.
9. Japan's high-end strip is in short supply. Due to the rapid development of copper strip industry in China, Japanese enterprises can only produce high-end copper strip for survival, such as copper-nickel-silicon series, copper-chromium-zirconium series, beryllium copper, titanium copper and so on. Japanese copper strip (excluding brass strip) production increased from 190000 tons in 1991 to 270000 tons in 2018, accounting for 33 per cent of the copper processing industry from 15 per cent. The increment mainly comes from: (1) semiconductor lead frame, etching type; (2) automobile connector; (3) low insertion force reflux tin plating process; (4) tin bronze, Corson alloy, titanium copper, beryllium copper for mobile phone. As a result of mergers and product upgrades, processing fees in the copper strip industry have risen.
10. Due to the improvement in demand and the growth of automotive electronics, Japanese companies have begun a new round of investment. Japanese companies are optimistic about the downstream: Internet of things, artificial intelligence, big data, self-driving, electric cars and other emerging industries such as semiconductors and sensors. These downstream will drive the demand for high-performance copper plate and strip for a long time.
Risk tips: copper strip downstream demand deteriorates; downstream technology updates quickly, enterprises are not up to pace; trade war intensifies; enterprise production and operation risks, and so on.
Copper strips for electrical connectors
The content of this chapter is mainly quoted from the speech of the conference: Yang Fen is "basic technical research on the application of contact copper" and Peng Lijun "systematic research on high-performance copper alloy materials for electrical connectors".
In typical equipment systems, many complex connectors and other interconnected devices are often found, including ordinary wires, equipment circuit boards, printed circuit connectors, backplane connections and interconnection cables. Generally speaking, the connection modes on electronic or electrical equipment can be divided into six types: the internal connection of components; the connection of components to printed circuit boards or wires; the connection of printed circuit boards to wires or other printed circuit boards (within the frame) on the internal frame of the same single machine; the connection from one internal frame to another in the same stand-alone box; the external connection from one stand-alone device to another; The connection between the system and the system.
The lead frame is the contact to realize the second type of connection. As the chip carrier of the integrated circuit, it realizes the electrical connection between the leading end of the internal circuit of the chip and the external wire with the help of bonding material, and acts as a bridge to connect with the external wire.
Lead frame and manufacturing and packaging application requirements, in addition to high strength, high thermal conductivity, but also requires good brazing, stamping, etching and oxide particle adhesion and so on. It is often made of copper-iron system, copper-nickel-silicon system C70250 and so on.
As an important downstream of copper plate and strip, connectors consume a large amount of plate and strip. The main performance requirements of connectors for copper strip are: high strength, high formability, high electrical conductivity and excellent stress relaxation resistance. Other properties are: fatigue performance, indicating quality and so on. The main copper plates for electrical connectors have the following:
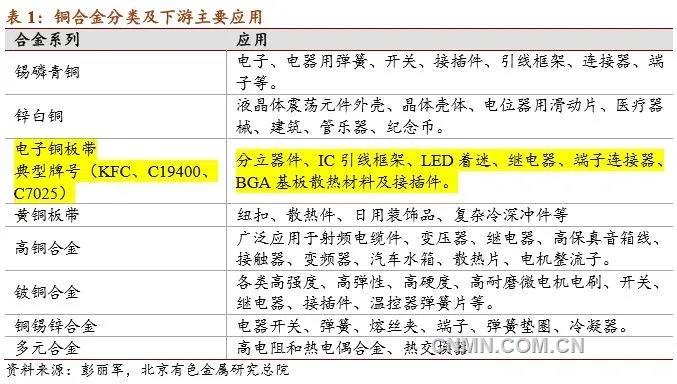
According to the strength and unit price, copper alloys can be divided as follows: high strength and easy forming alloy; medium and high strength and high conductivity alloy; medium and high strength alloy and general alloy. Cu-Ni-Si and Cu-Cr-Zr alloy strips belong to medium-high strength and high electrical conductivity alloys. Domestic Bowei alloy can be mass-produced, and Xingye Copper can mass-produce Cu-Ni-Si alloy. Beryllium copper (Cu-Be) can only be produced by oriental tantalum industry in China, but can not be supplied by Cu-Ti domestic companies. In particular, Cu-Ni-Si alloy has been widely used in the electronic field because of its excellent high temperature stability.
Cold deformation strengthening
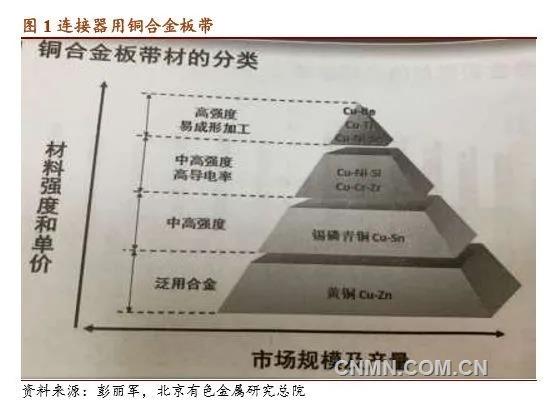
The common strengthening methods of contact copper materials are cold deformation strengthening, precipitation strengthening, excess phase strengthening and fine microstructure strengthening.
Cold deformation strengthening is also called cold work hardening, and the deformation of metal materials at recrystallization temperature is called cold deformation. The material is strengthened after cold deformation, and the strengthening strength varies with the degree of deformation, deformation temperature and the properties of the material itself.
Tin phosphorus bronzes such as C5191 and QSn4-3 of the same specification have higher tensile strength and hardness than brass such as H62 and HPb59-1. However, the cost of adding tin to tin phosphorus bronze is increased, and the electrical conductivity is low and the repeated bending property is poor. For this reason, C42500, C41125, PW33520 (exclusive patented products of Bowei alloy) and other high-performance and low-cost alternative products have been developed at home and abroad. Among them, the PW33502 alloy developed in China has a yield strength of 570Mpa and a conductivity of 34%, which is twice that of the original C5191, and can meet the requirements of high transmission and low temperature rise. The bending performance of the bad direction is also better than that of the original C5191. The tin content is lower than that of C5191, and the corner material of tin and nickel plating can be recycled. Compared with tin-phosphorus bronze, the comprehensive performance is excellent and the performance-to-price ratio is high.
Resistance to stress relaxation and heat resistance
Metal stress relaxation refers to the phenomenon that the total strain (elastic strain and plastic strain) remains unchanged and the stress decreases gradually with time under constant high temperature. The stress relaxation resistance of copper alloy used for contact parts is an important technical characteristic that determines whether the material can be applied reliably. Electrical connectors are often due to stress relaxation of Jack contact materials, resulting in poor contact or instantaneous power outage and other faults. Among them, C70250 has good resistance to stress relaxation.
The heat resistance of copper alloy materials used for contact parts is usually measured by measuring the change of contact pressure (stress relaxation) at the same temperature and for a long time. According to the Japanese JX company, after heating 150C for 1000 hours, the contact pressure of the connector is compared with that before heating. There are only 8% brass and 50% tin-phosphorus bronze. While copper-nickel-silicon alloy still has 80-90%, titanium-copper can keep 95%. However, the processing fee of titanium and copper is about 200,000 yuan per ton, which is much higher than that of copper, nickel and silicon (20,000-30,000 yuan per ton).
Car connectors are more heat-resistant than smartphones. The temperature environment inside the car: engine 120 ℃, engine surface 135 ℃, dashboard surface 120 ℃, interior floor 105 ℃, rear deck 117 ℃. When people ride in a car without air conditioning, the temperature inside the car can reach 120 ℃. The choice of brass and phosphorus bronze for automobile connectors has been unable to meet the requirements. Titanium-copper or copper-nickel-silicon with better stress relaxation resistance should be used.
High conductivity copper alloy
Copper alloy strips with high conductivity generally require yield strength above 500Mpa and electrical conductivity about 80%IACS. It is mainly used in high current connection situations, such as base station power connectors, new energy vehicle connectors and smart phone connectors. The amount of electricity of the connected machine inside the smart phone shows an increasing trend, which increases from 0.3A to 1.5-3.0A per core, which requires copper alloy to maintain a high level of strength and high electrical conductivity. The USBTYPE-C male terminal originally used C52100 tin-phosphorus bronze with a conductivity of 12% to produce a serious fever, but a highly conductive copper-nickel-silicon alloy with a conductivity of 65% can restrain the heating and temperature rise.
Application of Copper Alloy in equilibrium Direction
Generally speaking, the better the electrical conductivity of copper alloy is, the more difficult it is to maintain high strength. Copper alloy strip in equilibrium direction is mainly used in situations where there are certain requirements for material strength and electrical conductivity. generally, the yield strength is above 650Mpa and the electrical conductivity is about 65%IACS. For example, heavy-duty connectors and TYPE-C mother terminals require high electrical conductivity and good plug and pull resistance. Due to different user design concepts, some attach importance to electrical conductivity and some attach importance to yield strength, so there are two types of high conductive copper-nickel-silicon alloy for users to choose: electrical conductivity 65%IACS, yield strength 650Mpa, or electrical conductivity 90%, yield strength 490Mpa.
High strength directional copper alloy
High strength copper alloy strip generally requires yield strength above 900Mpa and electrical conductivity about 20%IACS. Mainly used for signal connection, such as VCM shrapnel, headphone shrapnel, SIM card connector and so on. The thickness of a manufacturer's smartphone has become more than 20% thinner in five years, so that most of the board-to-board connectors installed inside the phone are also flattened and finely spaced, and all other connectors are also required to be miniaturized. The mechanical strength and bending process formability of brass and tin-phosphorus bronze are difficult to meet the more and more stringent requirements. High-performance copper alloys such as copper-nickel-silicon alloy or titanium-copper alloy can meet the requirements of high strength, good bending processability and high electrical conductivity. Compared with the original tin-phosphorus bronze, copper-nickel-silicon alloy can increase the contact pressure by 12%, while titanium-copper can increase the contact pressure by 22%, compared with the original tin-phosphorus bronze, copper-nickel-silicon alloy or titanium-copper can increase the contact pressure by 12% and 22% respectively. The price of titanium and copper is much higher than that of copper, nickel and silicon, and the price of copper, nickel and silicon is relatively high.
Beryllium copper and its substitute materials
Beryllium copper has higher strength, stronger resistance to stress relaxation and elasticity than bronze and brass, and can provide the maximum force in limited space. It also has high electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, excellent corrosion resistance and good technological properties. It can be stamped in any direction under the condition of annealing and cold rolling. As a result, beryllium copper is widely used in aviation, aerospace and other high reliability connectors.
However, the production and smelting process of beryllium copper has serious pollution to the environment, and whether it will be gradually banned in the world has always been an issue for leaders and experts in the connector industry to pay attention to. In the case of strict environmental protection, the research and development of beryllium copper substitute materials has always been an issue of concern in the industry. The major copper processing enterprises in the world have successively developed alternative materials such as copper-nickel-tin series, copper-nickel-silicon system and titanium-copper alloy, which have been partially replaced.
II. Development trend of new copper alloy products
The content of this chapter is mainly quoted from the conference report: Ji Qing "Xingye Copper Industry New Copper Alloy Product release report".
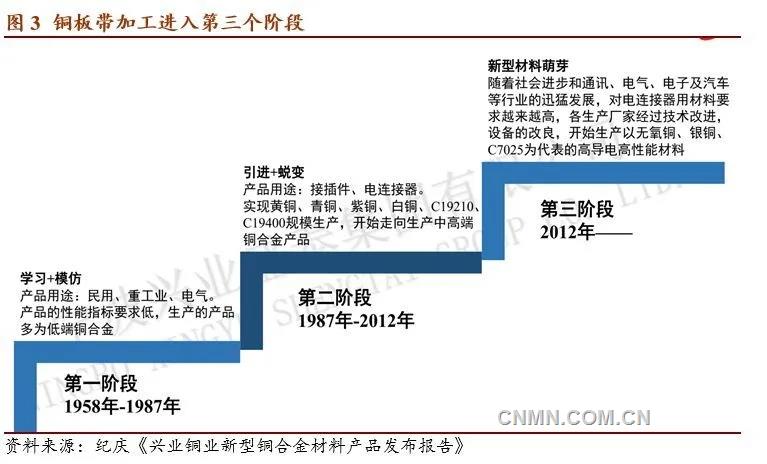
China's copper processing industry has gone through three stages, and now it has entered the stage of high-performance materials represented by C7025. Upgrade to meet the needs of industries such as communications, electronics and automobiles
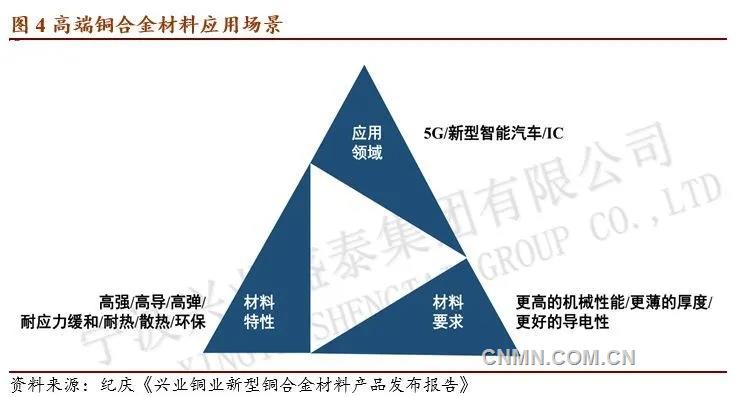
High-performance copper alloys should have high strength, excellent electrical conductivity, stress relaxation resistance and thermal conductivity. it is a necessary and urgently needed key basic material for aerospace, satellite navigation systems, 5G communications, new automobiles, network base stations, smart homes, large-scale integrated circuits and other key domains. high strength, high conductivity, high elasticity, high temperature resistance and stress relaxation resistance are very important properties of high performance copper alloys. Its preparation technology represents the advanced level of copper processing technology.
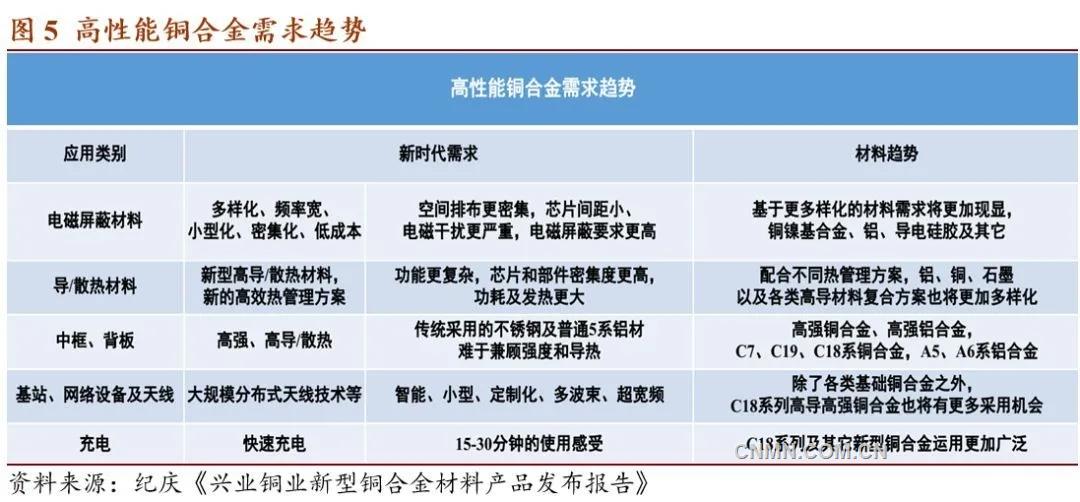
Xingye Shengtai developed C7026 and C7035 materials on the basis of C7025, in which C7035 has a strength of 900Mpa and a high electrical conductivity of 42-45% IACS. The production process is environmentally friendly and can be used as a substitute for low beryllium bronze.

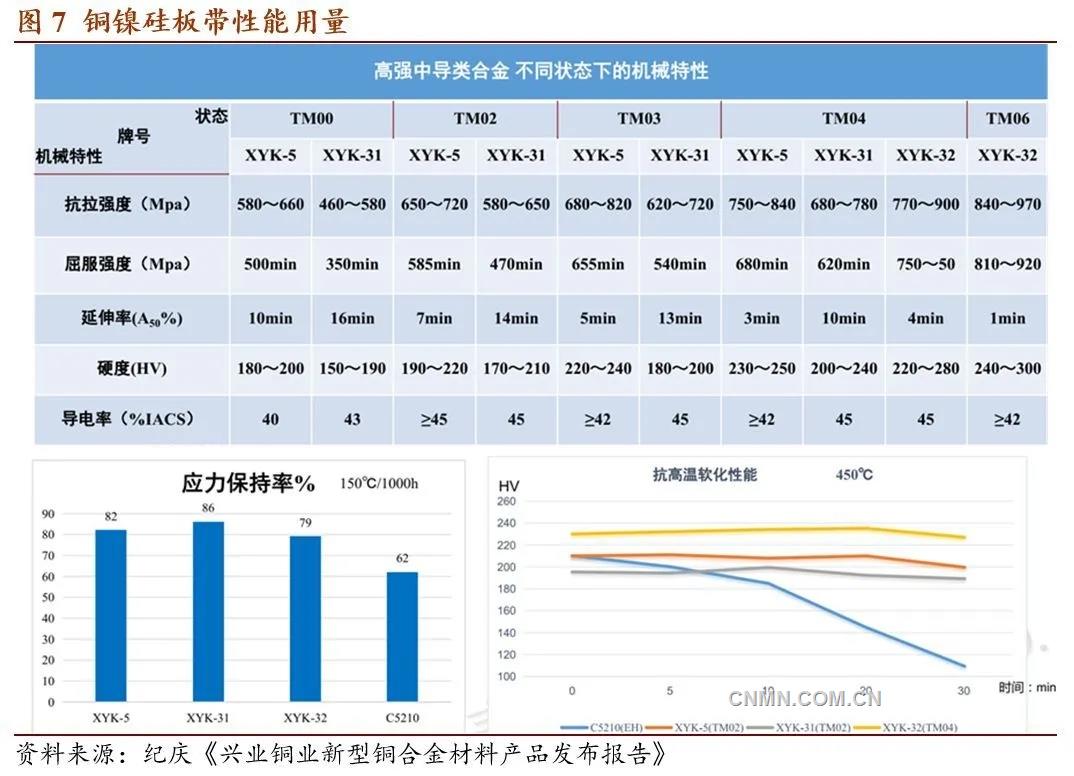
In the following data, XYK-5 stands for C7025 Magi XYKMur31 and C7026 for C7026. XYKMur32 represents C7035. These three materials not only have high strength and high electrical conductivity, but also have strong resistance to stress relaxation and high temperature softening.
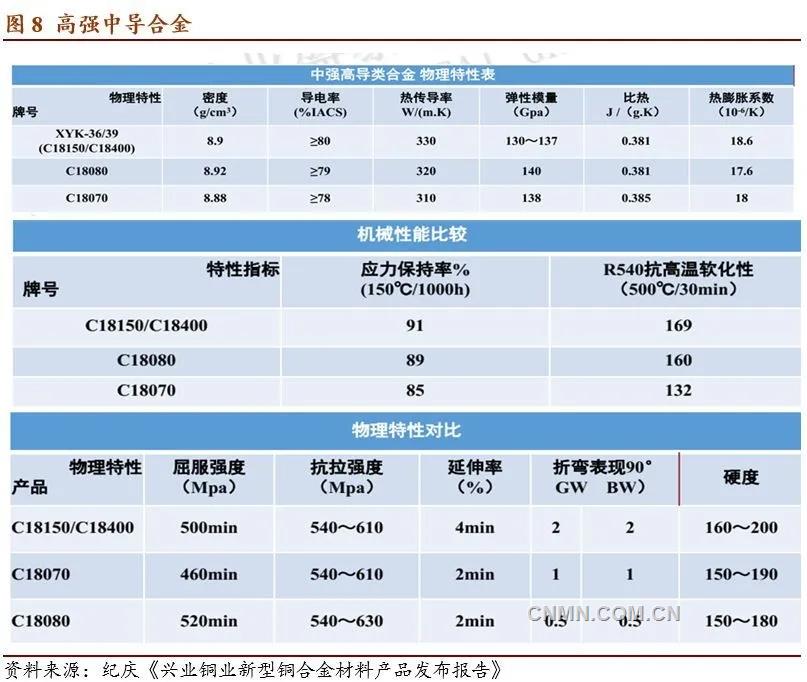
Medium strength and high conductivity alloys:
C18150Universe C18400Mel-strength 600MPa has both the electrical conductivity of 85%IACS and the thermal conductivity of 330W/ (m ·k). It is the most ideal copper alloy in the region of high electrical conductivity and medium strength, and has very high stress relaxation and high temperature softening resistance. Applications: high current connectors, oil-electric hybrid charge and discharge connectors, battery fast charge and flash charge, high power relays, terminals and preferred materials for efficient thermal management solutions.
The comparison of C18150/C18400, C18080 and C18070 shows that the elastic modulus of the three materials is basically similar, and the XYK-36 strength is higher than that of C18070 and C18080.
Under the condition of 150C / 1000h, the order of thermal stress relaxation rate is XYK-36 (C18150/C18400) > C18080 > C18070.
The order of high temperature softening resistance of 500C / 30min is XYK-36 (C18150/C18400) > C18080 > C18070.
The order of bending formability is C18080 > C18070 > XYK-36 (C18150/C18400).
The development of high performance copper alloy in the future may have the following four directions: (1) double 70 alloy, tensile strength 700MPa, electrical conductivity 70%IACS, thickness 0.03-0.06mm; (2) environment-friendly materials, tensile strength > 1000 MPa, yield strength > 950mm, electrical conductivity > 45% IACS; (3) new composite materials, making use of the characteristics and advantages of various metals, to improve the comprehensive properties and optimize the cost. (4) Magnetic conductive materials, CFA copper-iron alloy products, the general iron content is 15-50%.
III. Current situation of Copper processing Industry in Japan
In 1991, at the end of the bubble, Japan's copper processing output peaked at 1.2 million tons, surpassing the United States to become the first in the world. Of which 340000 tons are copper bars, 240000 tons are copper tubes, and 390000 tons are copper strips (including 200000 tons of brass belts). After 1991, Japan's copper processing production declined slightly, but remained at a level of about 1 million tons. In the 2008 financial crisis, it fell to 650000 tons and then recovered to a level of about 800000 tons, which has been maintained so far.
Several trends of Japanese copper processing industry in 2008: (1) merger. (2) transform the production of high value-added products.
From 2016 to 2018, plate and strip began to fall short of demand. The output of copper belt (excluding brass strip) increased from 190000 tons in 1991 to 270000 tons in 2018, accounting for 33 per cent of the total. The increment mainly comes from: (1) semiconductor lead frame, etching type; (2) automobile connector; (3) low insertion force reflux tin plating process; (4) tin bronze, Corson alloy, titanium copper, beryllium copper for mobile phone. As a result of mergers and product upgrades, processing fees in the copper strip industry have risen.
With the improvement of demand and the growth of automotive electronics, Japanese companies have begun a new round of investment. Japanese companies are optimistic about the downstream: Internet of things, artificial intelligence, big data, self-driving, electric cars and other emerging industries such as semiconductors and sensors. These downstream will drive the demand for high-performance copper plate and strip for a long time.
The output of major Japanese companies is as follows:
Kobe steel: monthly output of 4700-4800 tons, of which copper strip used in the electronic field accounts for 97%, exclusive alloy grades account for more than 75%.
Mitsubishi Copper extension: the production capacity is 4500 tons per month and the output is 4000 tons per month. Acquisition of YAMAHA (600-1200 tons per month), of which C7035100200 tons per month, 7025300 tons per month, C194100tons per month, titanium and copper 100tons per month.
JX Metals (Nippon Mining): production capacity: 4000 tons per month, including 1700 tons of tin bronze per month, 100tons of white copper per month, 200,300tons of tinned brass per month (ready to give up), 300tons of Corson alloy per month, 300tons of titanium and copper per month; there are also NKC164, NKC388, high strength NKT322 and high conductive NKT180.
IV. History of non-ferrous industry PE Band and PB Band
"Click to understand and sign up: 2020 China Automotive New Materials Application Summit Forum

Scan the QR code above to view the business cards of the participating companies and sign up online

Scan the code and apply to join the SMM Automotive Industry Exchange Group.



